Reconstructing the first successful lunar farside landing
In January of this year, China’s Chang’E-4 - the fourth version of a lunar spacecraft named for the Chinese goddess of the Moon - landed on the far side of the Moon. Due to the location of the landing, Chang’E-4 had to navigate autonomously, without the guidance of scientists on Earth.
Now, a research team, headed by Chunlai LI, corresponding author of this results and a professor of the National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), has published a full reconstruction of the Chang’E-4’s landing. The results appeared on September 24 in Nature Communications.
“This mission had the major challenge of landing on the lunar farside without traditional radio signal techniques due to the missing line-of-sight,” said Jianjun LIU, paper author and professor at the Key Laboratory of Lunar and Deep Space Exploration of NAOC. “The landing was successful, and we have now reconstructed the landing trajectory and positioning techniques to better understand the process.”
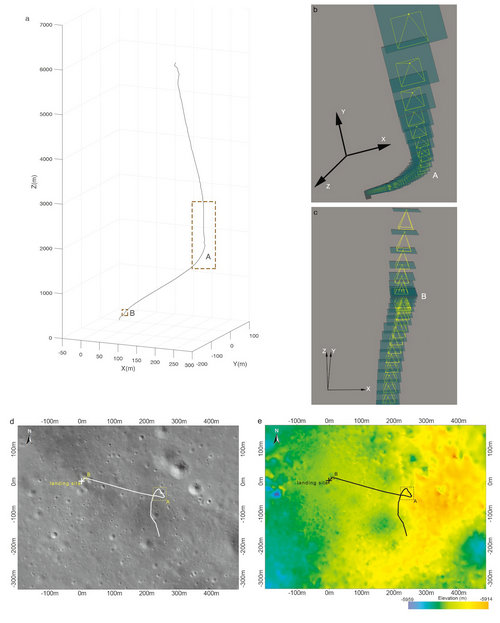
Fig.1: CE-4 powered descent trajectory (credit: NAOC)
Chang’E-4, which has spent 2019 collecting information about the geology of the Moon’s mantle, launched from Earth on December 8, 2018. Once it left Earth’s orbit, it circled the Moon before orchestrating a powered descent to the lunar surface, where it navigated itself to the Von Kármán crater, which sits in the South-Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin. The SPA basin stretches about 2,500 kilometers, or about half the width of China. It’s the largest known crater in the solar system.
The researchers planned for Chang’E-4 to land in the SPA basin because they’re specifically interested in studying the geological composition of the Moon. This is easier to do in areas where impacts may have penetrated past the lunar crust.
The problem was that the SPA basin contains several craters and is surrounded by even more. Previous versions of Chang’E had scouted out the location to a certain extent, so the researchers knew their ultimate landing site goal. However, it was up to Chang’E-4 to navigate around the steeper craters to land in the correct location.
After Chang’E-4 landed, images from the craft’s landing camera and navigation camera were transmitted to Earth via the Queqiao satellite. The satellite was launched in 2018 specifically to relay information from Chang’E-4 to Earth.
LI and his team used the images and terrain data from Chang’E-2 to identify the specific location of Chang’E-4, including the elevation down to the meter (-5,935 meters). They also fully reconstructed the path the lander took during its powered descent to the surface, during which it clearly navigated away from steeper craters to areas with flatter terrain.

Fig.2: Three-dimensional landscape map of the CE-4landing site (credit: NAOC)
“It’s of great significance to accurately reconstruct the landing trajectory and determine the location of the landing site after a safe landing,” LIU said. “We can use this information as landmarks and to service the study of lunar farside control points, high-precision lunar mapping, and future lunar missions.”
The paper was available at the following URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-12278-3
About The National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC):
The National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) was officially founded in April 2001 through the merger of observatories, stations and research center under Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is headquartered in Beijing and has four subordinate units across the country: the Yunnan Observatory (YNAO), the Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics and Technology (NIAOT), the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) and the Changchun Observatory.NAOC conducts cutting-edge astronomical studies, and operates major national facilities including The Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopy Telescope (LAMOST), the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) etc.
NAOC’s main research involves cosmological large-scale structures, the formation and evolution of galaxies and stars, high-energy astrophysics, solar magnetism and activity, lunar and deep space exploration, and astronomical instrumentation. NAOC has seven major research divisions in the areas of optical astronomy, radio astronomy, galaxies and cosmology, space science, solar physics, lunar and deep space exploration, and applications in astronomy.