A group led by researchers from Yunnan University has analyzed a large number of multi-epoch spectra obtained with the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST), and estimated the probabilities of the targets being radial velocity (RV) variables. The analysis yields a catalogue containing 80,702 RV variable candidates with probability greater than 0.60 based on the LAMOST DR4. These results have been published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series.
RV variable stars consist of intrinsic (e.g. pulsating stars) and extrinsic (e.g. binaries) variables. Identification and classification of RV variable stars can benefit many astrophysical studies. For example, for pulsating variable stars, such as RR Lyrae and Cepheids, along with their periodic contraction and expansion, their RVs will also show periodic variations. The relation between their photometric period and luminosity (absolute magnitude) can be used to accurately determine the distance, as a probe to the universe. For binary systems, the stellar parameters can be accurately determined through orbit solutions, which serve as independent benchmarks to constrain physical process inside the stars.
Meanwhile, compact objects such as white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes in binary systems could be detected through RV variations of their companion stars. In addition, the formation of some special stars can be attributed to binary evolution, e.g. a type Iasupernova originates from the material accretion of a white dwarf star from its companion star. Moreover, binary stars are also important for the study of stellar population synthesis.
Therefore, it is of great scientific significance to obtain RV variable stars including pulsating variable stars and binary stars. LAMOST is indeed an efficient facility to do this, which has been observing more and more RV variable stars repeatedly with its survey progressing.
This work has taken full advantage of the LAMOST huge dataset, and established the first RV variable star candidate catalogue based on the low-resolution spectroscopic survey data. Amongst the 80,702 stars in the catalogue, 77% are binaries and 7% pulsating stars, with purity higher than 80%. As an input catalogue, this RV variable star catalogue will play an important role in variable star surveys.
Dr. Zhijia Tian is the lead author, and Dr. Zhijia Tian and Prof. Xiaowei Liu the corresponding authors.
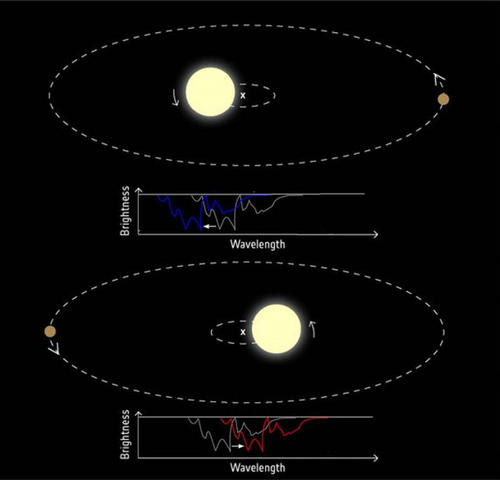
Figure: Cartoon picture showing how to detect the radial velocity variation.
The catalog, released as a value-added catalog for the LAMOST DR4 following the LAMOST Data Policy, is publicly available at http://dr4.lamost.org/v2/doc/vac.
The link to the source paper is at https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4365/ab9904.

Address: 20A Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China code: 100012
Tel: 010-64888708 E-mail: naoc@nao.cas.cn

