On June 30, 2018, LAMOST made its fourth Data Release (DR4) to astronomers worldwide, which includes all spectra obtained during the pilot survey and the first four years’ regular survey.
Through LAMOST DR4, a total number of 7.62 million spectra were released to the international community, which included 6.57 million high-quality spectra with SNR ≥ 10. Besides, a catalogue which as provided stellar parameters of 4.53 million stars was also released internationally in this data set. DR4 has thus resulted in the largest public spectral set and stellar parameter catalogue in the world at present.
According to the international practice, LAMOST DR4 is completely open to the world publically after the protection period. Any one that is interested in using LAMOST DR4 can log on the website at http//dr4.lamost.org/ to download this data set.
The huge data volume proves that LAMOST is indeed with the world’s highest spectral acquisition rate. Fig. 1 below shows the footprint of LAMOST pilot survey and the first four years’ regular survey.
LAMOST results in a final catalogue of about 10 million spectra after its six-year regular survey, which is an exceedingly valuable resource for a variety of astronomical fields. With the obtained data, scientists create a “digital Galaxy” for future research on the structure, formation and evolution of Galaxy. As Gaia and LAMOST sky survey move on smoothly, the near-future Galactic astronomy will enter a whole new era of LAMOST and Gaia.
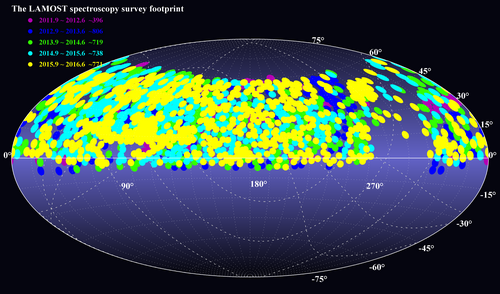
Fig. 1 shows the footprint of LAMOST pilot survey and the first four years’ regular survey.

Address: 20A Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China code: 100012
Tel: 010-64888708 E-mail: naoc@nao.cas.cn

