On a clear night in 1785, William Herschel used his own telescope to observe as usual. The difference is that this night he found a very unusual celestial object in Corvus (the Antennae Galaxy, Fig. 1). Since then, such kind of celestial objects, called the merging galaxies, have fascinated countless astronomers. How is it formed? How does it evolve? These questions are hot topics in astronomy today.
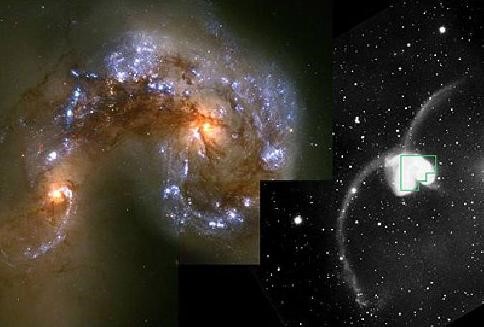
Fig.1. Antennae Galaxy. This merging galaxy is first discovered by William Herschel (Credit: Hubble Space Telescope, NASA)
Nowadays, more than 200 years later, scientists have been able to reproduce the formation process of the merging galaxies with numerical simulations. Because of the gravitational attraction, two galaxies would first approach each other, which are observed as a galaxy pair in this phase. Then, the violent collision process leads to dramatic changes on the shapes of the galaxies, thus forming special structures that are significantly different from normal galaxies (see Fig. 2 for an illustration).
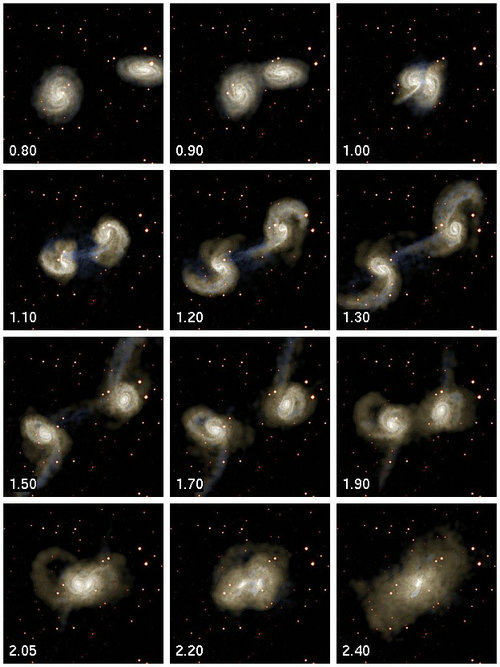

Fig. 2: Galaxy merging process from numerical simulation. The time (in billions of years since the beginning of the simulation) is indicated by the number in each picture. (Credit: Max-Planck Institute of Astrophysics)
Recently, a research team from Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (SHAO) published a new research result on galaxy pairs, which has been accepted by the Astrophysical Journal. In this study, they first constructed the largest galaxy pair sample to date, and then accurately measured the bivariate luminosity function of galaxy pairs. Prof. Shiyin Shen, the corresponding author of this work said, “the bivariate luminosity function tells us a whole story on what is the probability of a galaxy that could be paired with another galaxy at given luminosities, and also gives us hints on how often galaxy merging event occurs in the nearby universe.”
As shown by the numerical simulation, the merging timescale of two galaxies is up to 1-2 Giga years. Thus, the overall process of galaxy merging event could not be fully observed by human beings. Using the bivariate luminosity function of galaxy pairs as a statistical approach, this work probably has found the first observational evidence on the galaxy merging timescale. “The global timescale from two gravitational bounded galaxies to final merging depends on the mass configuration of two galaxies”, Shuai Feng, the first author of this study further explained, who is a Ph.D student supervised by Prof. Shiyin Shen, “typically, two massive galaxies with equal mass merge most quickly.”
In this work, besides the public astronomical database, the Guoshoujing Telescope (also known as LAMOST), which is located in Xinglong Station of National Astronomical Observatory of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), has made a significant contribution. For two very close galaxies on the sky like a galaxy pair, a regular multi-fiber spectroscopic survey (like Sloan Digital Sky Survey, also known as SDSS) typically can only target one of the members due to fiber collisions. One of the important observational samples of the LAMOST spectral survey is to supplement the missed main sample galaxies in the SDSS. The combination of the two surveys constitutes the largest spectroscopic identified galaxy pair sample so far, thus providing the foundation of this innovative statistical study.
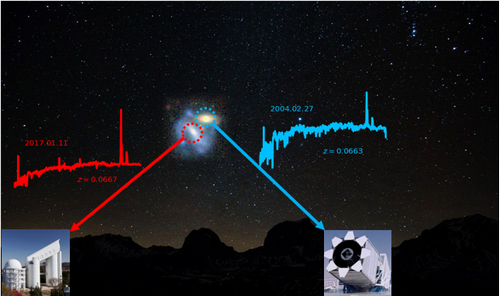
Fig. 3: An example of the spectroscopic observation of a galaxy pair. The spectroscopic observations of two very close galaxies were completed by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (blue) and the LAMOST spectral survey (red) respectively. Only by obtaining the spectroscopic distances of two galaxies can we finally identify whether two galaxies are a genuine pair or accidentally caused by projection effect.
Online link: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.07276

Address: 20A Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China code: 100012
Tel: 010-64888708 E-mail: naoc@nao.cas.cn

